Get ready to dive into the world of Understanding mutual funds with a fresh perspective that will leave you wanting more. This topic is about to get a serious makeover with a touch of American high school hip style.
Let’s break it down and discover the ins and outs of mutual funds in a way that’s both informative and fun.
What are mutual funds?
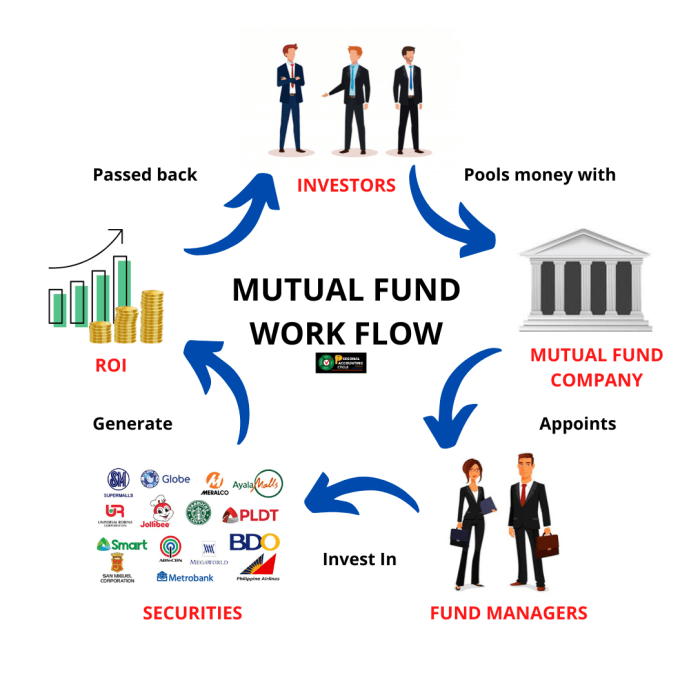
Mutual funds are investment vehicles that pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities. They are managed by professional fund managers who make investment decisions on behalf of the investors.
Types of mutual funds
There are several types of mutual funds available to investors, each with its own investment objective and risk profile:
- Equity Funds: These funds invest primarily in stocks and are suited for investors seeking long-term growth.
- Bond Funds: These funds invest in fixed-income securities like government or corporate bonds, offering steady income and lower risk compared to stocks.
- Money Market Funds: These funds invest in short-term, low-risk securities like Treasury bills and certificates of deposit, providing stability and liquidity.
- Index Funds: These funds aim to replicate the performance of a specific market index, such as the S&P 500, offering broad market exposure at low costs.
- Balanced Funds: These funds invest in a mix of stocks and bonds to provide a balanced approach to growth and income.
Benefits of investing in mutual funds
Investing in mutual funds offers several advantages to investors:
- Professional Management: Mutual funds are managed by experienced professionals who make investment decisions based on research and analysis.
- Diversification: By investing in a mutual fund, investors gain exposure to a diversified portfolio of securities, reducing the risk of individual stock or bond picking.
- Liquidity: Mutual funds allow investors to buy and sell shares on any business day, providing liquidity compared to individual securities.
- Accessibility: Mutual funds are accessible to investors with different risk profiles and investment goals, making them suitable for a wide range of investors.
Understanding mutual fund fees
Mutual fund fees are charges that investors pay for the management and operation of the fund. These fees can have a significant impact on the overall return on investment, so it’s important to understand them before investing.
Expense ratios are one type of fee associated with mutual funds. This ratio represents the percentage of the fund’s assets that are used to cover operating expenses. A lower expense ratio is generally favorable for investors, as it means more of the fund’s returns are being passed on to them.
Sales loads are another type of fee that investors may encounter when investing in mutual funds. These are charges that investors pay either when buying (front-end load) or selling (back-end load) shares of a fund. It’s important to consider these fees, as they can eat into your returns over time.
Comparison of expense ratios and sales loads
- Expense ratios: Typically range from 0.05% to 2% or more, depending on the type of fund.
- Sales loads: Front-end loads can be around 3-5% of the investment amount, while back-end loads may decline over time if you hold the fund for a certain period.
Fees can significantly impact the overall return on investment. For example, if you invest $10,000 in a fund with a 1% expense ratio and it earns a 7% return, your actual return would be 6% after accounting for fees. Therefore, it’s crucial to consider fees when evaluating the potential returns of a mutual fund.
How to select a mutual fund
When it comes to selecting a mutual fund that aligns with your financial goals, there are several key factors to consider. From the management style to the fund’s performance history, making an informed decision is crucial to maximizing your investment potential.
Actively managed funds vs. passively managed funds
Actively managed funds are overseen by fund managers who make decisions to buy and sell securities in an attempt to outperform the market. On the other hand, passively managed funds aim to replicate the performance of a specific market index. While actively managed funds may have higher fees due to the active management involved, passively managed funds often have lower fees and may be more predictable in terms of returns.
Researching the fund’s performance history
Before investing in a mutual fund, it’s essential to research the fund’s performance history. Look at how the fund has performed compared to its benchmark index over different time periods. Analyze the fund’s consistency in delivering returns and consider factors like volatility and risk-adjusted returns. By understanding the fund’s past performance, you can make a more informed decision about its potential for future growth.
Risks associated with mutual funds
Investing in mutual funds comes with certain risks that investors should be aware of in order to make informed decisions. Understanding these risks can help investors navigate the ups and downs of the market and potentially minimize losses.
Market Risk
Market risk is the potential for an investment to lose value due to factors affecting the overall performance of the financial markets. This type of risk is inherent in all types of investments, including mutual funds. Factors such as economic conditions, geopolitical events, and market volatility can impact the value of mutual fund investments.
Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate risk refers to the impact that changes in interest rates can have on the value of fixed-income securities held within a mutual fund. When interest rates rise, the value of existing bonds held by the fund may decrease. Conversely, when interest rates fall, bond values may rise. This risk is particularly relevant for bond funds.
Credit Risk
Credit risk is the risk of a borrower failing to repay a loan or bond, resulting in a loss for the lender or bondholder. Mutual funds that invest in corporate bonds or lower-quality debt securities are exposed to credit risk. If a bond issuer defaults on its payments, it can negatively impact the mutual fund’s performance.
Diversification is a key strategy used to mitigate risks in mutual fund investments. By spreading investments across different asset classes, sectors, and regions, investors can reduce the impact of any single investment performing poorly. Diversification helps to balance out the risks associated with individual holdings, providing a more stable overall portfolio.