Diving deep into the world of market cycles, this introduction sets the stage for a fascinating exploration of how these cycles impact industries and investments. Get ready to ride the wave of information about Understanding market cycles in a way that’s fresh, engaging, and totally rad!
Let’s break down the different phases, factors, types, and strategies that make up the complex world of market cycles.
Overview of Market Cycles
Market cycles are a crucial concept in the financial world, representing the repetitive patterns of growth and decline in financial markets. Understanding these cycles is essential for investors and analysts to make informed decisions and navigate the ups and downs of the market.
Phases of a Market Cycle
- The Accumulation Phase: This is the initial stage where smart money starts buying assets at low prices, anticipating future growth.
- The Markup Phase: Prices begin to rise as more investors enter the market, driving up demand.
- The Distribution Phase: Smart money starts selling their holdings to profit from the peak prices, leading to a decrease in demand.
- The Decline Phase: Prices start to fall as supply exceeds demand, leading to a market downturn.
- The Panic Phase: Fear grips the market, and prices plummet drastically as investors rush to sell off their assets.
Impact of Market Cycles on Industries
- Real Estate: Market cycles can greatly impact the real estate industry, with periods of booming growth followed by downturns affecting property values and demand.
- Technology: Tech companies often experience rapid growth during the markup phase of a market cycle, only to face challenges during the decline phase when consumer spending decreases.
- Commodities: The prices of commodities such as oil, gold, and agricultural products are heavily influenced by market cycles, leading to fluctuations in supply and demand.
Factors Influencing Market Cycles
Market cycles are influenced by a variety of factors that impact the overall direction and behavior of financial markets. These factors can range from economic indicators to investor sentiment, all playing a crucial role in shaping market cycles.
Economic Indicators
Economic indicators are essential tools used by analysts and investors to assess the health of an economy. These indicators provide valuable insights into the current state of the economy, such as GDP growth, inflation rates, employment levels, and consumer spending. Changes in these indicators can signal shifts in market cycles, as they reflect the overall economic conditions that drive investor behavior.
- Economic indicators such as GDP growth can indicate the strength of an economy, influencing investor confidence and market sentiment.
- Inflation rates can impact interest rates set by central banks, affecting borrowing costs and investment decisions in the market.
- Unemployment levels can influence consumer spending and overall economic activity, leading to changes in market cycles.
Investor Sentiment
Investor sentiment refers to the collective attitude and emotions of investors towards the market. This sentiment can often be a driving force behind market cycles, as investor behavior is influenced by perceptions of risk, uncertainty, and opportunity.
- Positive investor sentiment can lead to bullish market conditions, with increased buying activity and rising asset prices.
- Negative investor sentiment, on the other hand, can trigger bearish market trends, characterized by selling pressure and declining prices.
- Market cycles can experience shifts in response to changes in investor sentiment, as market participants react to news, events, and broader economic conditions.
Types of Market Cycles
When it comes to market cycles, there are different types that investors should be aware of. Understanding the distinctions between short-term and long-term market cycles, as well as the characteristics of bull and bear markets, can help investors make more informed decisions.
Short-term vs. Long-term Market Cycles
Short-term market cycles typically last for a few weeks to a few months and are influenced by factors such as investor sentiment, economic data releases, and geopolitical events. These cycles are characterized by quick fluctuations in prices and trading volumes.
On the other hand, long-term market cycles can span several years or even decades. They are influenced by broader economic trends, such as interest rates, inflation, and overall market conditions. Long-term cycles tend to have more sustained trends in prices and are often associated with major economic shifts.
Bull and Bear Markets
Bull markets are characterized by rising prices, investor optimism, and overall positive sentiment. During a bull market, investors are confident in the economy and are willing to take on more risk. Bull markets are typically associated with strong economic growth and low unemployment rates.
Conversely, bear markets are marked by falling prices, pessimism, and a general lack of confidence in the market. Bear markets are often accompanied by economic downturns, high levels of uncertainty, and rising unemployment rates. Investors in bear markets tend to be more risk-averse and may seek safer investment options.
Distinct Market Cycles Across Assets or Sectors
Different assets or sectors can experience distinct market cycles based on their underlying fundamentals and external influences. For example, technology stocks may go through cycles of innovation and disruption, leading to rapid price changes. Real estate markets may experience cycles of boom and bust based on factors like interest rates and housing demand.
Understanding how different assets or sectors behave within market cycles can help investors diversify their portfolios and manage risk effectively.
Strategies for Navigating Market Cycles
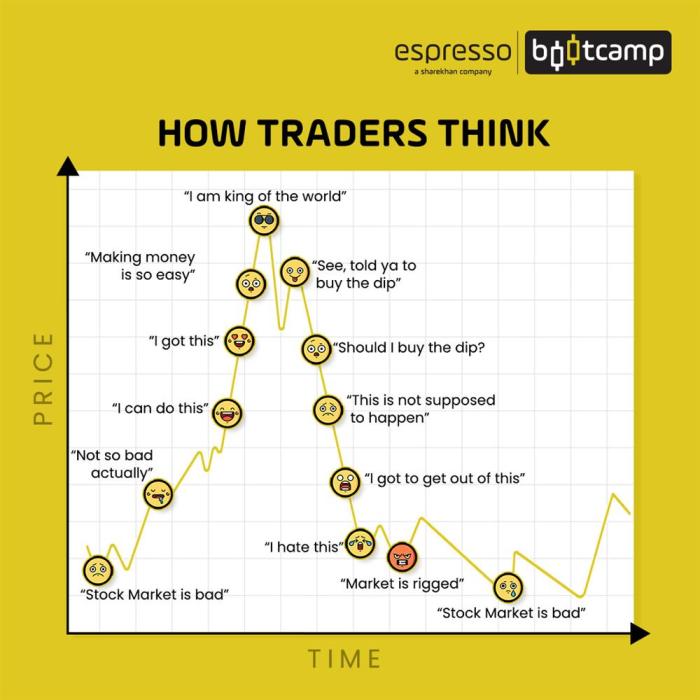
As an investor, navigating market cycles can be challenging, but having the right strategies in place can help you make informed decisions. Here are some tips to help you navigate market cycles effectively:
Identifying the Current Phase of a Market Cycle
Understanding the current phase of a market cycle is crucial for making investment decisions. Here are some tips to help you identify where the market stands:
- Monitor economic indicators and trends to gauge the overall health of the economy.
- Pay attention to market sentiment and investor behavior, as these can provide clues about the direction of the market.
- Study historical market data to identify patterns and trends that may indicate the current phase of the cycle.
Diversification Strategies to Mitigate Risks
Diversification is key to mitigating risks during different market cycles. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Spread your investments across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, to reduce exposure to any single market.
- Consider investing in international markets to diversify your portfolio and reduce risk associated with domestic market fluctuations.
- Rebalance your portfolio regularly to ensure that your asset allocation aligns with your risk tolerance and investment goals.
Contrarian Investing and Its Relevance
Contrarian investing involves going against the crowd and investing in assets that are currently out of favor. Here’s why it’s relevant in various market cycles:
- Contrarian investing can help you capitalize on market inefficiencies and identify opportunities that others may overlook.
- By taking a contrarian approach, you may be able to buy assets at a lower price when they are undervalued and sell them at a higher price when sentiment shifts.
- However, contrarian investing also comes with risks, so it’s important to conduct thorough research and analysis before making investment decisions.