Hey there, ready to dive into the world of student loan interest rate calculation? Grab your backpack and get ready for a wild ride through the ins and outs of how those interest rates are calculated. It’s gonna be lit!
In this guide, you’ll uncover the mysteries behind student loan interest rates, from understanding the factors that influence them to exploring different calculation methods. So, buckle up and let’s roll!
Understanding Student Loan Interest Rate Calculation
When it comes to student loans, understanding how interest rates are calculated is crucial. Let’s break it down.
Factors Influencing Student Loan Interest Rates
Interest rates on student loans are influenced by several factors, including the type of loan, the lender, the borrower’s credit history, and the current market conditions. Lenders also consider the loan term and whether the loan is subsidized or unsubsidized.
Difference Between Fixed and Variable Interest Rates
Fixed interest rates remain the same throughout the life of the loan, providing stability in monthly payments. On the other hand, variable interest rates can fluctuate based on market conditions, potentially leading to lower initial rates but higher payments in the future.
Interest Accrual During Different Periods
Interest on student loans accrues differently during various periods. While in-school, grace, or deferment periods, interest may be subsidized or deferred. However, during the repayment period, interest accrues on the outstanding balance, affecting the total amount repaid over time.
Expression of Student Loan Interest Rates
Student loan interest rates are typically expressed as Annual Percentage Rate (APR) or simple interest rates. APR includes both the interest rate and any additional fees, giving borrowers a comprehensive view of the total cost of borrowing. Simple interest rates, on the other hand, only consider the interest charged on the principal amount borrowed.
Formula for Calculating Student Loan Interest
When it comes to understanding student loan interest rates, it’s crucial to grasp the formula used to calculate the interest on these loans. This formula takes into account the loan balance, interest rate, and the time period over which the loan is held. Let’s break it down step by step to see how these variables impact the total interest accrued.
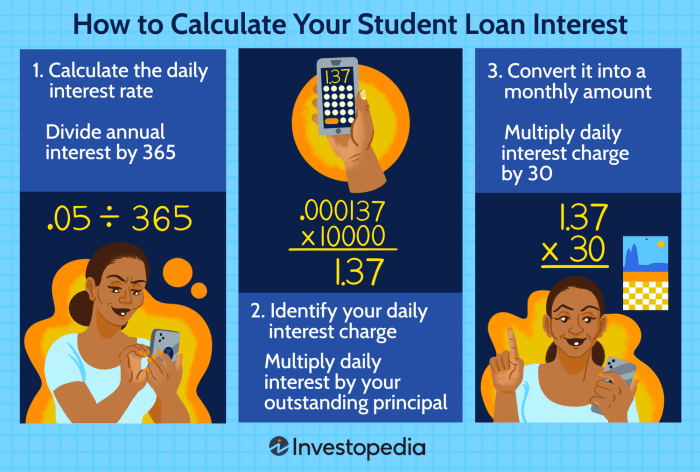
Concept of Daily Interest Accrual
Daily interest accrual is a key concept in calculating interest on student loans. Instead of calculating interest on a monthly basis, daily interest accrual breaks it down into smaller increments. This means that the interest is calculated based on the outstanding balance each day, leading to a more accurate representation of the interest accrued.
- Calculate the Daily Interest Rate: To start, divide the annual interest rate by the number of days in a year to get the daily interest rate.
- Calculate the Daily Interest Amount: Multiply the daily interest rate by the remaining balance to determine the interest accrued for that day.
- Accumulate Daily Interest: Repeat the process for each day, adding the daily interest amounts to get the total interest accrued over the specified time period.
Remember, the lower the remaining balance and the shorter the time period, the less interest you will pay.
Impact of Interest Rate on Student Loan Repayment
When it comes to student loan repayment, the interest rate plays a crucial role in determining the total amount you’ll end up paying over time. Understanding how different interest rates can affect your repayment journey is essential for managing your finances effectively.
How Interest Rates Affect Total Amount Repaid
The interest rate on your student loan directly impacts the total amount you repay. A higher interest rate means you’ll end up paying more over the life of the loan. For example, a 6% interest rate on a $30,000 loan will result in more interest paid compared to a 4% interest rate on the same amount.
- Higher interest rates lead to higher monthly payments, making it harder to pay off the loan.
- Lower interest rates can help reduce the total amount repaid and shorten the repayment period.
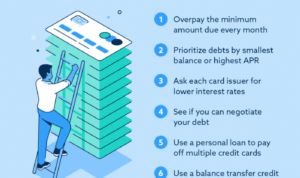
Minimizing the Impact of High-Interest Rates
To minimize the impact of high-interest rates on student loan repayment, consider the following strategies:
- Make extra payments towards the principal to reduce the overall interest paid.
- Refinance your student loans to secure a lower interest rate and potentially save money over time.
- Explore income-driven repayment plans that adjust your monthly payments based on your income level.
Refinancing and Consolidating Student Loans
Refinancing or consolidating your student loans can be a smart move to lower your interest rates and make repayment more manageable. By combining multiple loans into one with a lower interest rate, you can save money and simplify your repayment process.
Refinancing your student loans can help you secure a lower interest rate, potentially saving you thousands of dollars over the life of the loan.
Real-Life Examples of Interest Rate Impact
Let’s consider a real-life example: A borrower with a $50,000 student loan at a 7% interest rate will end up paying more in interest compared to the same loan amount at a 4% interest rate. The difference in monthly payments and overall repayment amount can be significant over time.
- At 7% interest rate: Total repayment amount = $65,000
- At 4% interest rate: Total repayment amount = $56,000
Comparing Interest Rate Calculation Methods
When it comes to calculating interest on student loans, lenders use different methods that can impact the total amount borrowers end up paying. Let’s dive into the comparison of these calculation methods to understand the pros and cons of each.
Simple Interest vs. Compound Interest
Simple interest is calculated only on the principal amount borrowed, while compound interest takes into account both the principal and any accrued interest. Here’s a breakdown of the pros and cons of each:
- Simple Interest:
- Pros: Easier to understand, lower total interest paid in the long run.
- Cons: Higher initial payments, may not reflect true cost of borrowing.
- Compound Interest:
- Pros: Accurately reflects the cost of borrowing, can lead to higher total interest paid.
- Cons: More complex to calculate, higher overall cost for borrowers.
Impact of Compounding Periods
The frequency at which interest is compounded, whether daily, monthly, or annually, can significantly affect the total interest paid on a student loan. Here’s how different compounding periods can impact borrowers:
- Daily Compounding: Results in the highest total interest paid due to more frequent calculations.
- Monthly Compounding: Offers a middle ground between daily and annual compounding in terms of total interest paid.
- Annual Compounding: Results in the lowest total interest paid but may not be as accurate in reflecting the true cost of borrowing.
Choosing the Right Calculation Method
Depending on individual circumstances, one calculation method may be more beneficial than others for borrowers. For example:
For borrowers looking to minimize the total interest paid and prioritize lower monthly payments, simple interest may be the better option. On the other hand, those who want a more accurate representation of the cost of borrowing may opt for compound interest with annual compounding.