With structured financial products at the forefront, this paragraph opens a window to an amazing start and intrigue, inviting readers to embark on a storytelling journey filled with unexpected twists and insights.
Structured financial products are a complex yet fascinating area of finance that offer unique opportunities for investors seeking tailored investment solutions. From the different types available to the process of creation and the associated benefits and risks, there’s a lot to explore in this dynamic landscape.
What are structured financial products?
Structured financial products are investment instruments created by combining traditional assets like stocks and bonds with derivatives in order to offer customized risk-return profiles to investors. These products are designed to meet specific investment objectives or risk tolerance levels of investors.
Types of structured financial products
- Structured Notes: These are debt securities with embedded derivatives that provide a return linked to the performance of an underlying asset.
- Structured Certificates: These are similar to structured notes but are issued by a financial institution and may offer principal protection or enhanced returns based on the performance of the underlying asset.
- Structured Deposits: These are bank deposits with an embedded derivative component that offers a return based on the performance of an underlying asset.
- Structured Funds: These are investment funds that use derivatives to enhance returns or manage risk in the portfolio.
Characteristics of structured financial products
Structured financial products have several key characteristics that distinguish them from traditional financial products. These characteristics include complexity, customization, and embedded derivatives.
Complexity
Structured financial products are often complex in nature, combining different financial instruments to create a unique investment opportunity. This complexity can make it challenging for investors to fully understand the product and its associated risks.
Customization
One of the main features of structured financial products is their customization. These products are tailored to meet the specific needs and objectives of individual investors, allowing them to choose the underlying assets, risk levels, and payout structures that align with their investment goals.
Embedded Derivatives
Structured financial products typically include embedded derivatives, such as options or swaps, which can enhance returns or provide downside protection. These derivatives are used to create unique payoff profiles that may not be achievable with traditional investments.
Difference from Traditional Financial Products
Structured financial products differ from traditional financial products in terms of their complexity, customization, and risk-return profile. Unlike traditional investments like stocks or bonds, structured products offer investors a wider range of investment strategies and risk management techniques.
Risk-Return Profile
The risk-return profile associated with structured financial products varies depending on the underlying assets and structure of the product. These products can offer potentially higher returns than traditional investments, but they also come with increased complexity and risks. Investors should carefully evaluate the risk-return trade-off before investing in structured products to ensure they align with their investment objectives and risk tolerance.
How are structured financial products created?
Structured financial products are created through a meticulous process that involves financial institutions, market experts, and investors. These products are designed to meet specific investment objectives and risk profiles.
Role of financial institutions
Financial institutions play a crucial role in structuring financial products by analyzing market trends, investor preferences, and risk appetite. They work closely with investment bankers, traders, and legal experts to design products that align with the needs of their clients.
- Financial institutions conduct thorough market research to identify opportunities for creating structured products that offer unique investment strategies.
- They collaborate with experts in quantitative analysis to develop models that assess the potential risks and returns of the structured products.
- Financial institutions also ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and provide ongoing support to investors who purchase these products.
By leveraging their expertise and resources, financial institutions can tailor structured products to address the specific needs of individual investors or institutions.
Factors considered when designing structured financial products
When designing structured financial products, several key factors are taken into consideration to ensure that the products meet the desired objectives and risk profiles of investors.
| 1. Market conditions: | Financial institutions assess current market conditions and trends to determine the most suitable investment strategies for structured products. |
| 2. Investor preferences: | Understanding the risk tolerance, investment goals, and preferences of investors is essential in designing products that align with their needs. |
| 3. Regulatory requirements: | Compliance with regulatory frameworks and guidelines is a critical consideration when structuring financial products to ensure transparency and investor protection. |
| 4. Risk management: | Effective risk management strategies are integrated into the design of structured products to mitigate potential risks and enhance investor confidence. |
Benefits and drawbacks of structured financial products
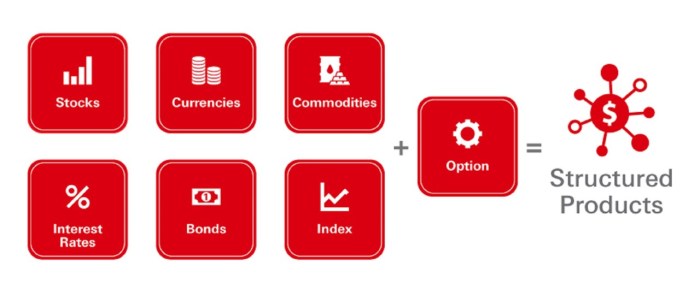
Structured financial products offer investors a unique set of benefits that can help diversify their portfolios and potentially enhance returns. These products are designed to provide tailored solutions to meet specific investment objectives, offering a combination of different assets and strategies that traditional investments may not provide. Some of the advantages include:
Advantages of investing in structured financial products:
- Customization: Investors can tailor the product to their risk tolerance, return objectives, and market views.
- Diversification: Structured products can provide exposure to a wide range of asset classes and markets.
- Potential for enhanced returns: Some structured products offer the opportunity for higher returns compared to traditional investments.
- Risk management: These products can be structured to provide downside protection or limit potential losses.
However, it’s important to consider the potential drawbacks and risks associated with structured financial products. Some of the key concerns include:
Drawbacks or risks associated with structured financial products:
- Complexity: Structured products can be difficult to understand due to their intricate design and use of derivatives.
- Lack of liquidity: Some structured products may have limited liquidity, making it challenging to sell them before maturity.
- Counterparty risk: Investors are exposed to the credit risk of the issuer, as structured products are typically issued by financial institutions.
- Costs: Structured products may involve higher fees and costs compared to traditional investments.
When comparing structured financial products to other investment options, it’s essential to weigh the benefits and drawbacks. While structured products offer unique features and potential advantages, investors should carefully assess their risk tolerance, investment goals, and understanding of these complex products before investing.