Get ready to dive into the world of 401(k) vs. IRA, where the battle for the best retirement account unfolds like a classic high school rivalry. Buckle up and let’s explore the ins and outs of these financial powerhouses!
401(k) Overview
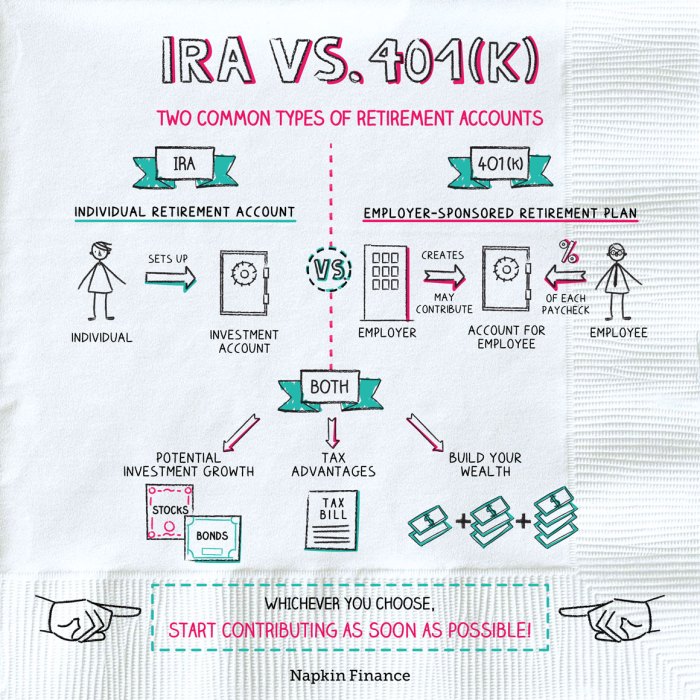
A 401(k) retirement account is a type of employer-sponsored retirement savings plan that allows employees to contribute a portion of their paycheck to a tax-advantaged investment account for retirement.
Key Features and Benefits
- Employer matching contributions: Some employers match a portion of the employee’s contributions, which can help boost retirement savings.
- Tax advantages: Contributions are made on a pre-tax basis, reducing taxable income, and investment growth is tax-deferred until withdrawals are made in retirement.
- Automatic payroll deductions: Contributions are deducted directly from the employee’s paycheck, making saving for retirement convenient.
Eligibility Criteria
To participate in a 401(k) plan, employees must usually meet the following criteria:
- Be at least 21 years old
- Have completed at least one year of service with the employer
- Work a minimum number of hours per week as defined by the employer
Contribution Limits
The contribution limits for a 401(k) account are set by the IRS and can vary each year. For 2021, the contribution limit is $19,500 for individuals under 50 years old, with a catch-up contribution of $6,500 for those 50 and older. These limits are higher than other retirement accounts like IRAs, providing an opportunity for greater savings.
IRA Overview
An Individual Retirement Account (IRA) is a type of retirement savings account that allows individuals to save for their retirement with tax advantages.
Types of IRAs
- Traditional IRA: Contributions are typically tax-deductible, and withdrawals are taxed as income in retirement.
- Roth IRA: Contributions are made with after-tax dollars, and withdrawals in retirement are tax-free.
- SEP IRA: Simplified Employee Pension IRA for self-employed individuals or small business owners.
- SIMPLE IRA: Savings Incentive Match Plan for Employees IRA for small businesses with fewer than 100 employees.
Contribution Limits and Tax Advantages
- Contribution Limits: For 2021, the annual contribution limit for IRAs is $6,000 ($7,000 if age 50 or older).
- Tax Advantages: Traditional IRA contributions may be tax-deductible, reducing taxable income, while Roth IRA contributions grow tax-free.
Flexibility of IRAs vs. 401(k) Plans
IRAs offer more flexibility compared to 401(k) plans in terms of investment options and withdrawal rules. With IRAs, individuals have more control over their investments and can withdraw funds penalty-free for certain expenses like education or first-time home purchase.
401(k) vs. IRA: Investment Options
In a 401(k) plan, the investment options are typically limited to a selection of mutual funds, stocks, bonds, and sometimes target-date funds. These options are chosen by the employer or plan administrator and can vary in risk and return potential.
401(k) Investment Options
401(k) plans usually offer a range of investment choices such as:
- Stocks: Investing in individual company stocks for potential growth.
- Bonds: Fixed-income securities offering steady returns.
- Mutual Funds: Pooled investments in various assets managed by professionals.
- Target-Date Funds: Automatically adjusting asset allocation based on the investor’s retirement date.
It is essential to consider the risk tolerance and investment goals when choosing among these options in a 401(k) plan.
IRA Investment Choices
Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) provide more flexibility in investment options compared to 401(k) plans. Investors can choose from a broader range of investments, including stocks, bonds, mutual funds, ETFs, real estate, and even precious metals.
- ETFs: Exchange-traded funds that track various indices or sectors.
- Real Estate: Direct ownership of properties or real estate investment trusts (REITs).
- Precious Metals: Investing in gold, silver, or other valuable metals for diversification.
IRAs allow investors to create a customized investment portfolio based on their risk tolerance and financial objectives.
Risks in 401(k) and IRA Investments
Investing in both 401(k) and IRA accounts carry inherent risks, such as market volatility, inflation, and geopolitical events. However, 401(k) plans may have limited investment options, leading to less diversification and potentially higher risk if not managed properly.
Impact of Investment Decisions on Retirement Savings
The investment decisions made within a 401(k) or IRA can significantly impact the growth of retirement savings over time. Choosing high-risk investments may result in higher returns but also higher volatility, while conservative investments offer stability but lower potential returns. It is crucial to regularly review and adjust investment choices based on changing financial goals and market conditions to maximize retirement savings.
Tax Implications
When it comes to saving for retirement, understanding the tax implications of different accounts is crucial. Let’s explore how taxes can impact your 401(k) and IRA.
401(k) Contributions
- Contributions to a traditional 401(k) plan are made with pre-tax dollars, meaning you can deduct the amount from your taxable income in the year you contribute.
- This reduces your current tax liability, allowing you to save more for retirement while potentially lowering your tax bill.
- However, withdrawals from a traditional 401(k) in retirement are taxed as ordinary income at your current tax rate.
IRA Contributions
- Contributions to a traditional IRA are also made with pre-tax dollars, providing similar tax benefits as a 401(k) in terms of reducing your taxable income.
- Like a 401(k), withdrawals from a traditional IRA are taxed as ordinary income in retirement.
Withdrawals Comparison
- One key difference between a 401(k) and an IRA is the required minimum distributions (RMDs) that begin at age 72 for traditional accounts.
- Failure to take RMDs can result in substantial penalties, so it’s crucial to understand the rules for each account.
Impact on Growth
- Taxes can significantly impact the growth of your retirement savings in both a 401(k) and an IRA.
- By minimizing taxes on contributions and strategically managing withdrawals, you can maximize the growth potential of your retirement accounts.