Diving into the world of loan amortization schedule, we uncover the intricate details that shape the financial landscape for borrowers. Brace yourself for a journey filled with insights and revelations that will change the way you view loan repayments.
As we delve deeper, we’ll explore the fundamentals of loan amortization schedules and how they play a crucial role in managing finances effectively.
What is a loan amortization schedule?
A loan amortization schedule is a table that details the periodic payments made towards a loan over time. It breaks down each payment into the principal amount and the interest, showing how much of each payment goes towards reducing the loan balance and how much goes towards paying the interest.
How a loan amortization schedule works
A loan amortization schedule works by calculating the monthly payments needed to pay off a loan within a specific period. These payments are structured so that in the initial stages of the loan, more of the payment goes towards paying off the interest, while in the later stages, more goes towards reducing the principal amount.
- The components of a loan amortization schedule include:
- Principal: The initial amount borrowed, which decreases with each payment.
- Interest: The cost of borrowing the principal amount, which decreases as the principal is paid off.
- Monthly Payment: The total amount due each month, comprising both principal and interest.
- Remaining Balance: The outstanding loan amount yet to be paid off after each payment.
Importance of understanding loan amortization schedules
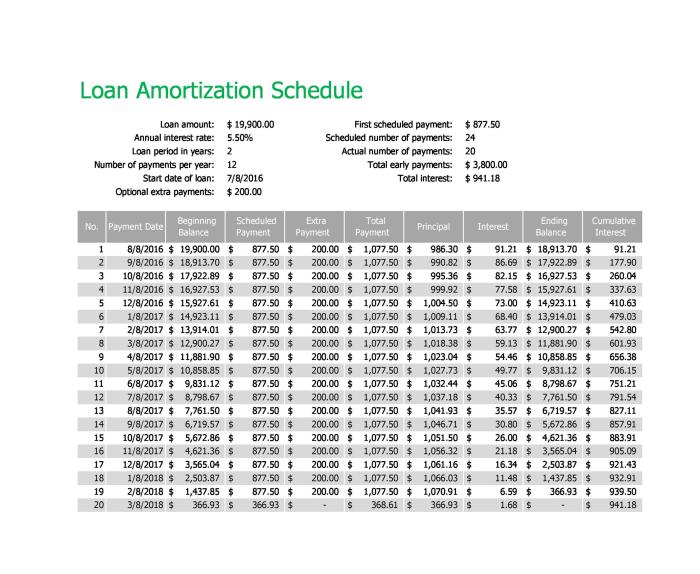
Understanding loan amortization schedules is crucial for borrowers because it provides clarity on how their loan payments are structured over time. By knowing how much of each payment goes towards interest and principal, borrowers can make informed decisions about their finances.
Financial Planning
Having a clear understanding of loan amortization schedules can greatly help in financial planning. Borrowers can anticipate future payments, budget effectively, and even consider making extra payments to reduce the overall interest paid over the life of the loan.
Impact on Loan Repayment
Loan amortization schedules have a significant impact on loan repayment. In the early years of a loan, a larger portion of each payment goes towards interest, while in later years, more goes towards paying down the principal. This information can help borrowers see the long-term effects of their loan and make decisions accordingly.
Calculating loan amortization schedules
When it comes to calculating loan amortization schedules, you need to break it down step by step to understand how it all works. Let’s dive into the process of manual calculation, the formula used for monthly payments, and the impact of interest rates and loan terms.
Calculating a loan amortization schedule manually
To calculate a loan amortization schedule manually, you will need to follow these steps:
- Determine the loan amount, interest rate, and loan term.
- Calculate the monthly interest rate by dividing the annual interest rate by 12.
- Use the formula for calculating monthly loan payments:
Monthly Payment = P[r(1+r)^n]/[(1+r)^n-1]
Where:
- P = Loan amount
- r = Monthly interest rate
- n = Total number of payments
- Calculate the monthly payment using the formula.
- Repeat the calculation for each month to create the loan amortization schedule.
Explaining the formula used for calculating monthly loan payments
The formula for calculating monthly loan payments takes into account the loan amount, interest rate, and loan term. By plugging in these values, you can determine the fixed monthly payment required to pay off the loan over the specified period. Understanding this formula is crucial for managing your finances and planning your budget effectively.
Role of interest rates and loan terms in the calculation
Interest rates and loan terms play a significant role in determining the monthly payment amount and the total cost of the loan. A higher interest rate will result in higher monthly payments, while a longer loan term will spread out the payments over a longer period but may increase the total interest paid. It’s essential to consider these factors when calculating loan amortization schedules to make informed financial decisions.
Differences between fixed and variable loan amortization schedules
When it comes to loan amortization schedules, there are two main types to consider: fixed-rate and variable-rate schedules. Each type has its own unique characteristics and can impact your financial situation differently.
Fixed-rate Loan Amortization Schedule:
Fixed-rate Loan Amortization Schedule
A fixed-rate loan amortization schedule is one where the interest rate remains the same throughout the life of the loan. This means that your monthly payments will also remain constant, providing predictability and stability in your budgeting.
- Interest rates do not change over time, providing consistency in monthly payments.
- Easy to budget for since payments remain the same each month.
- Offers peace of mind as you know exactly what to expect in terms of payments.
Example: If you have a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage at 4% interest, your monthly payment will stay the same for the entire 30-year term.
Variable-rate Loan Amortization Schedule:
Variable-rate Loan Amortization Schedule
A variable-rate loan amortization schedule, on the other hand, has an interest rate that can fluctuate based on market conditions. This means that your monthly payments can vary over time, potentially affecting your budget and financial planning.
- Interest rates can change periodically, leading to fluctuations in monthly payments.
- Initial lower interest rates may result in lower initial payments, but payments can increase if rates rise.
- May offer potential cost savings if interest rates decrease over time.
Example: With a variable-rate mortgage, your initial payments may be lower if interest rates are low, but they could increase if rates go up in the future.
Advantages and Disadvantages:
Advantages and Disadvantages
Both fixed-rate and variable-rate loan amortization schedules have their own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these can help you make an informed decision based on your financial goals and risk tolerance.
- Fixed-rate schedules provide stability and predictability but may come with higher initial interest rates.
- Variable-rate schedules offer potential cost savings but come with the risk of payments increasing if interest rates rise.
- Choosing between the two depends on your financial situation, risk tolerance, and future interest rate expectations.