Diving into the world of debt-to-income ratio explained, we unravel the complexities of this financial metric that plays a crucial role in determining your financial health. Get ready to explore the ins and outs of how your debts stack up against your income, and why it’s a key factor in your financial well-being.
As we delve deeper, you’ll gain a better understanding of how this ratio impacts your financial decisions and what steps you can take to ensure a healthy financial future.
Understanding Debt-to-Income Ratio
When it comes to managing your finances, understanding your debt-to-income ratio is crucial. This ratio is a key indicator of your financial health and helps lenders assess your ability to repay loans.
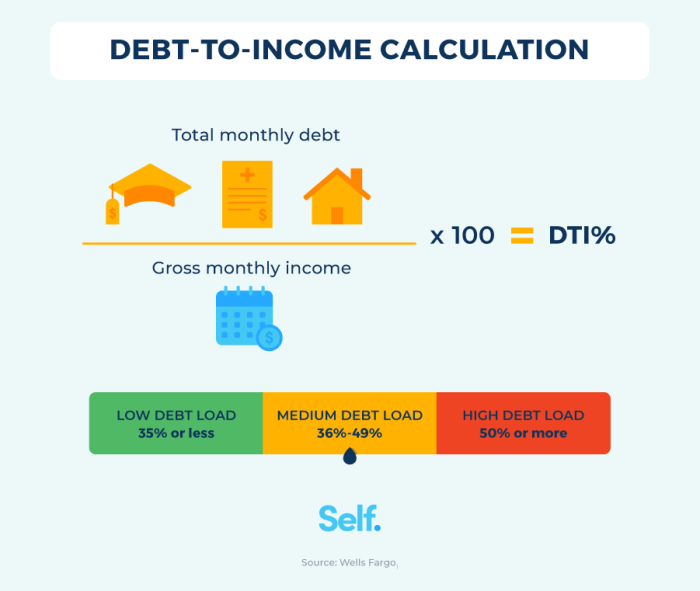
Debt-to-income ratio is a financial term that compares the amount of debt you owe to the amount of income you earn. It is expressed as a percentage and is calculated by dividing your total monthly debt payments by your gross monthly income.
Importance of Debt-to-Income Ratio
Maintaining a healthy debt-to-income ratio is important because it gives lenders insight into your ability to manage debt and make timely payments. A lower ratio indicates that you have more income available to meet your debt obligations, making you a lower credit risk.
- For example, if your total monthly debt payments amount to $1,500 and your gross monthly income is $5,000, your debt-to-income ratio would be calculated as follows:
Debt-to-Income Ratio = (Total Monthly Debt Payments / Gross Monthly Income) x 100%
Debt-to-Income Ratio = ($1,500 / $5,000) x 100% = 30%
- Aim to keep your debt-to-income ratio below 36% to qualify for most loans and demonstrate financial stability.
Significance of Debt-to-Income Ratio
Debt-to-Income Ratio plays a crucial role in determining an individual’s financial health and stability. Lenders often use this ratio to evaluate loan applications and assess the borrower’s ability to manage additional debt responsibly.
Importance of Debt-to-Income Ratio for Lenders
- Lenders use the debt-to-income ratio to gauge the borrower’s capacity to repay a loan based on their current income and existing debt obligations.
- A lower debt-to-income ratio indicates that the borrower has more disposable income available to meet their monthly loan payments, making them a lower credit risk.
- By analyzing the debt-to-income ratio, lenders can make informed decisions on approving or denying loan applications and determining the appropriate loan amount and interest rate.
Ideal Debt-to-Income Ratio Range
- The ideal debt-to-income ratio for financial health is typically below 36%. This means that no more than 36% of a borrower’s gross monthly income should go towards paying off debts.
- Having a lower debt-to-income ratio not only improves the chances of loan approval but also indicates good financial management and the ability to live within one’s means.
- Individuals with a debt-to-income ratio below 20% are considered to have excellent financial health and are more likely to qualify for favorable loan terms.
Impact of High Debt-to-Income Ratio
- A high debt-to-income ratio, above 43%, can signal financial distress and may result in difficulties in obtaining new credit or loans.
- Individuals with a high debt-to-income ratio may struggle to make timely payments on their existing debts, leading to late fees, increased interest rates, and a negative impact on their credit score.
- Moreover, a high debt-to-income ratio limits the individual’s ability to save for the future, invest, or handle unexpected expenses, ultimately compromising their financial stability.
Factors Affecting Debt-to-Income Ratio
When it comes to understanding debt-to-income ratio, it’s crucial to consider the various factors that can affect this financial metric. The components of debt-to-income ratio, the impact of different types of debt, and how changes in income levels can influence this ratio are all key aspects to explore.
Components of Debt-to-Income Ratio
- Debt: This includes all monthly debt payments such as credit card bills, student loans, car loans, and mortgage payments.
- Income: This refers to your total monthly income before taxes, which can come from sources like salaries, bonuses, commissions, and rental income.
Types of Debt and Their Influence on Ratio
- Credit Card Debt: High credit card balances can significantly increase your debt-to-income ratio, especially if you only pay the minimum amount each month.
- Student Loans: Student loan payments can also impact the ratio, with higher monthly payments leading to a higher ratio.
- Mortgage Debt: The amount of your mortgage payments relative to your income can have a substantial effect on your debt-to-income ratio.
Impact of Changes in Income Levels
- Increasing Income: A rise in income can lower your debt-to-income ratio, making you appear less risky to lenders.
- Decreasing Income: Conversely, a decrease in income can raise your ratio, potentially affecting your ability to borrow money or secure favorable interest rates.
Managing Debt-to-Income Ratio
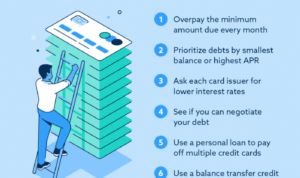
When it comes to managing your debt-to-income ratio, there are several strategies you can implement to improve your financial health and achieve a favorable ratio. Budgeting plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy balance between your debt and income, while reducing debt is essential for long-term financial stability.
Importance of Budgeting
Budgeting is key to managing your debt-to-income ratio effectively. By creating a detailed budget that Artikels your income and expenses, you can identify areas where you can cut back on spending and allocate more funds towards paying off debt. This proactive approach helps you stay on track with your financial goals and prevents you from accumulating more debt than you can afford.
- Track your income and expenses meticulously to understand where your money is going.
- Set realistic financial goals and prioritize debt repayment in your budget.
- Avoid unnecessary expenses and focus on needs rather than wants.
- Regularly review and adjust your budget to accommodate changes in your financial situation.
Tips for Reducing Debt
Reducing your debt is essential for improving your debt-to-income ratio and achieving a more favorable financial standing. Here are some tips to help you reduce your debt effectively:
- Create a debt repayment plan: Prioritize high-interest debt and pay more than the minimum amount due.
- Consider debt consolidation to combine multiple debts into one lower-interest payment.
- Negotiate with creditors for lower interest rates or payment plans that fit your budget.
- Avoid taking on new debt and focus on paying off existing balances.