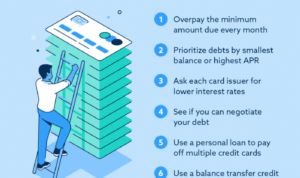
Diving into the world of retirement plan options, this introduction sets the stage for an epic journey through the realm of financial planning. From 401(k) to pension plans, get ready to unlock the secrets to securing your future like a boss.
Get ready to roll with the pros and cons of each retirement plan type as we break it down in a language that even your grandma can understand.
Types of Retirement Plans
When it comes to planning for retirement, there are several options to choose from. Let’s dive into the different types of retirement plans available and how they work in practice.
401(k) Plan
- A 401(k) plan is a retirement savings account offered by employers.
- Employees can contribute a portion of their salary to the plan, often with a matching contribution from the employer.
- Investment options within a 401(k) plan typically include stocks, bonds, and mutual funds.
- Withdrawals from a 401(k) are usually taxed as income in retirement.
Individual Retirement Account (IRA)
- An IRA is a retirement account individuals can open independently.
- There are different types of IRAs, including traditional IRAs and Roth IRAs, each with unique tax advantages.
- Contributions to a traditional IRA may be tax-deductible, while withdrawals in retirement are taxed as income.
- Roth IRAs allow for tax-free withdrawals in retirement, but contributions are made with after-tax dollars.
Pension Plans
- Pension plans are retirement plans funded by employers that provide a fixed monthly benefit upon retirement.
- Employees typically do not make contributions to pension plans; instead, the employer funds the plan.
- Pension plans offer a guaranteed income stream in retirement, which can be a valuable source of financial security.
- Some pension plans may have eligibility requirements based on years of service with the company.
Understanding 401(k) Plans
401(k) plans are popular retirement savings vehicles offered by employers to help employees save for their golden years. These plans allow employees to contribute a portion of their pre-tax salary into a retirement account, which can then be invested to grow over time.
Key Features of 401(k) Plans
- Contributions: Employees can contribute a percentage of their salary to their 401(k) account, up to the annual contribution limit set by the IRS.
- Employer Matches: Some employers offer matching contributions to employee 401(k) accounts, which can help boost retirement savings significantly.
- Investment Options: 401(k) plans typically offer a variety of investment options, such as mutual funds, stocks, and bonds, allowing employees to choose how their money is invested.
Maximizing 401(k) Benefits
- Take Advantage of Employer Match: Contribute enough to your 401(k) to maximize your employer’s match, as this is essentially free money added to your retirement savings.
- Increase Contributions Over Time: Aim to increase your contributions to your 401(k) as your income grows or whenever you receive a raise to accelerate your retirement savings.
- Diversify Investments: Spread your investments across different asset classes within your 401(k) to reduce risk and potentially increase returns over the long term.
Exploring Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs)

When it comes to saving for retirement, Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) are a popular choice. IRAs offer tax advantages and flexibility in managing your retirement savings.
Types of IRAs
- Traditional IRA: A traditional IRA allows you to make tax-deductible contributions, and your investments grow tax-deferred until withdrawal during retirement.
- Roth IRA: With a Roth IRA, contributions are made with after-tax dollars, but withdrawals in retirement are tax-free, including investment earnings.
- SEP IRA: A Simplified Employee Pension (SEP) IRA is designed for self-employed individuals or small business owners to make tax-deductible contributions for themselves and their employees.
Eligibility and Contribution Limits
- Traditional IRA: Anyone under 70 ½ years old with earned income can contribute, with a maximum contribution limit of $6,000 (for 2021).
- Roth IRA: Income limits apply for Roth IRAs, with a contribution limit of $6,000 (for 2021) for those under certain income thresholds.
- SEP IRA: Self-employed individuals and small business owners can contribute up to the lesser of 25% of compensation or $58,000 (for 2021).
Using IRAs for Retirement Savings and Investment
IRAs can be powerful tools for building a retirement nest egg. For example, you can invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, and mutual funds within your IRA to help grow your savings over time. Additionally, IRAs provide a way to save for retirement on top of employer-sponsored plans like 401(k)s.
Pension Plans and Social Security
Retirement planning involves various options to secure financial stability in your golden years. Pension plans and Social Security are two key components that play a significant role in retirement income.
Pension Plans vs. Other Retirement Savings Options
Pension plans differ from other retirement savings options in that they are typically employer-sponsored and provide a fixed amount of income based on factors like salary and years of service. Unlike 401(k) plans or IRAs, pension plans do not involve individual contributions, as the employer funds the plan.
Social Security in Retirement Planning
Social Security is a federal program designed to provide a safety net for retired individuals. It is funded through payroll taxes and offers benefits based on your earnings history. Social Security benefits can be a crucial source of income during retirement, especially for those without substantial savings or pension plans.
Pension Plans vs. Social Security for Retirement Income
When comparing pension plans and Social Security for retirement income, it’s essential to consider the benefits and limitations of each. Pension plans offer a guaranteed income stream, but they are dependent on the financial health of the employer. On the other hand, Social Security provides a reliable source of income, but the benefits may not be sufficient to cover all expenses in retirement.
In conclusion, both pension plans and Social Security play vital roles in retirement planning. It’s crucial to diversify your sources of income to ensure financial stability during your retirement years.